Bioeconomy - For a Sustainable Economy
Leather alternatives made from apple scraps, insulating materials made from hemp or pet food made from insects. Bioeconomy products are innovative, sustainable and often follow very creative approaches. Numerous players in Saxony are working on solutions for a sustainable economy across all sectors.

Infomodul
Facts about the bioeconomy in Saxony
-
18.000
The company -
177.000
Employees -
9.000 / 13.000
Apprentices / Students -
99
Research institutes
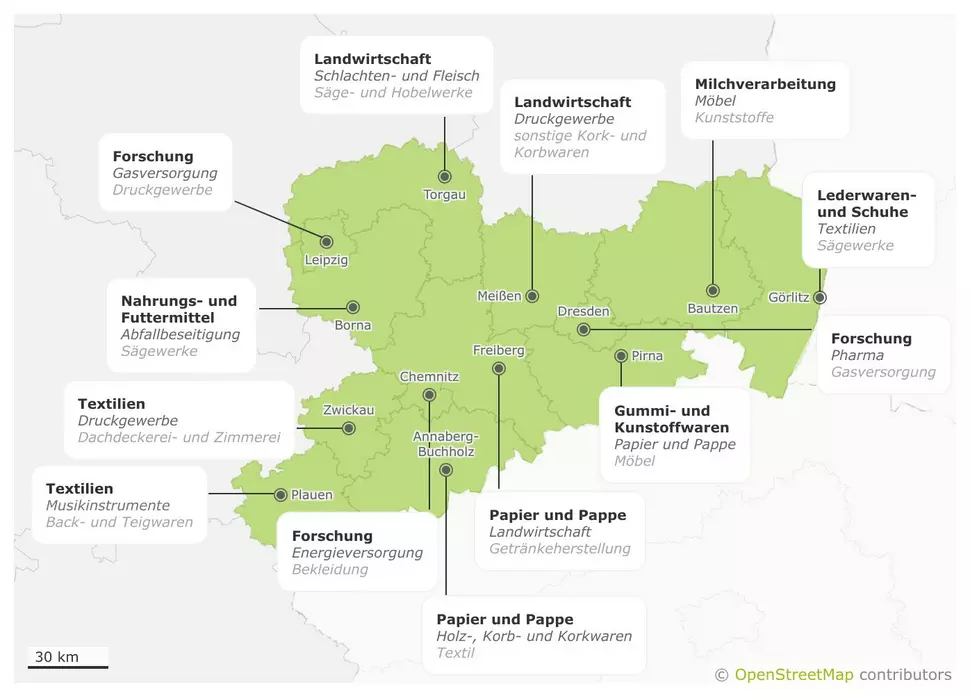
Bioeconomy ecosystem in Saxony
Saxony as a business location can be further expanded and made more sustainable with the help of the bio-based economy. By efficiently linking the production and processing of raw materials, the development/testing of new technologies and new business models, Saxony's regions can develop into strong bioeconomy clusters.
Companies
The range of sectors that belong to the bioeconomy is broad. The focus in Saxony is on the production of food and animal feed, agriculture and construction. The textile industry, which processes organic raw materials such as hemp or linen fibers into suitable products, and the life sciences sector are also of particular importance.
The agricultural business of Agrargenossenschaft "Bergland" Clausnitz e. G. makes optimum use of material and energy cycles. Milk production and the cultivation of crops (cereals, rapeseed and fiber crops) are the main economic pillars of the farm. Energy production also takes center stage. The farm produces its own biogas, wind and solar energy and can thus supply its own infrastructure. Rapeseed cultivation supplies cows with food and agricultural machinery with biofuel.
Agrargenossenschaft „Bergland“ Clausnitz e. G.
Natural fibers are suitable for the production of a wide range of products. As yarns, tapes or in the form of high-performance fibers, they can be used in a wide range of industries. SachsenLeinen GmbH in Markkleeberg develops key solutions along supply chains and natural fibers for a wide range of applications and markets.
SachsenLeinen GmbH
With its innovative product lines, madebymade GmbH from Pegau makes an important contribution to sustainability and resource-conserving production. The company produces proteins and fats that are obtained from insects. The maggots from Saxony are thus conquering the market as animal feed, fertilizer or in the form of palm oil substitutes.
madebymade GmbH
fit "Grüne Kraft" washing-up liquid, tabs and household cleaners come from Zittau. For over 50 years, fit GmbH has been making German households cleaner with its cleaning products. With its products, the company focuses on a responsible approach to the environment as well as cost- and energy-saving production processes. Part of the product range consists of biodegradable ingredients based on citric acid or palm oil.
fit GmbH
Vogtlandmilch GmbH in Plauen is supplied with around 220 million kg of milk annually by around 260 farmers from the Vogtland region, western Saxony and eastern Thuringia. The company uses the milk to produce a wide range of dairy products and soft drinks, which are known under the brands "Vogtlandweide" and "Sachsenland". At the Plauen site, the aim is to convert even more to environmentally friendly and sustainable production in the future. The company received investment funds of 13.85 million euros from the Free State of Saxony in 2022 for this purpose.
Vogtlandmilch GmbH
The start-up nevi GmbH specializes in the processing of birch bark for the construction industry. The company from Görlitz develops attractive veneers, handles and furniture surfaces from this native tree species. The raw material birch bark is harvested by hand and used sustainably in the region. Together with the Fraunhofer Institute for Microstructure of Materials and Systems IMWS, nevi is currently developing an adhesive system with up to 90 percent biogenic ingredients.
nevi GmbH
Research
There are around 100 research facilities and institutes in Saxony that conduct all or part of their research on bioeconomy topics. Fundamental and application-oriented research in the life and technical sciences are central to the bioeconomy. The economic, social, political and legal sciences are also important pillars for a holistic approach.
The German Biomass Research Center (DBFZ), founded in 2008, develops practical solutions along the biomass value chains and cycles. Through applied research and development (R&D) of technologies for the energetic and integrated material use of biomass, the DBFZ contributes to the realization of a climate-neutral society.
German Biomass Research Center (DBFZ)
The focus of the work at the Helmholtz Center for Environmental Research GmbH (UFZ) in Leipzig is on research into the transformation processes of the entire economic system. Bioeconomy research at the UFZ is concerned with innovative (bio)technological processes aimed at the production of energy sources and valuable materials from sunlight and CO2, electricity and residual or waste materials (cellulose, lignocellulose, by-products of chemical and biotechnical synthesis) that have only been used to a limited extent to date.
Helmholtz Center for Environmental Research GmbH (UFZ)
The German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) is a research center of the German Research Foundation (DFG) with main locations in Halle, Jena and Leipzig. Here, researchers from 40 nations develop the scientific basis for the sustainable management of our planet's biodiversity.
German Center for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv)
The Helmholtz Center Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) strives to gain new insights in order to preserve and improve the basis of our existence. To this end, research in the fields of energy, health and matter is carried out at the HZDR in Dresden and other locations.
Helmholtz Center Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR)
The Fraunhofer Institute for Process Engineering and Packaging IVV is a leader in applied research for the secure supply of high-quality food and for sustainable packaging systems. At its Dresden site, the Fraunhofer IVV develops efficient processing and cleaning processes. Product safety and process efficiency are the most important aspects in the development of processing systems.
Fraunhofer Institute for Process Engineering and Packaging IVV, Dresden site
Politics: Future mission bioeconomy
The great potential of the bioeconomy, biotechnology and biopharma for Saxony as a business location is confirmed by an outlook published by the Saxon Innovation Advisory Board in 2021.
Saxony's state government is integrating the bioeconomy into the update of its 2020 innovation strategy. Located in the future field of "environment", it is classified as an overarching approach with which a sustainable contribution can be made in the areas of recycling management, agriculture and forestry, raw materials management and energy. Particularly high innovation potential is attributed to bio-based processes in the efficient use of biogenic waste materials. Phosphorus recovery from wastewater serves as an example.
As one of ten future missions, the bioeconomy is also part of the "Mission Saxony 2038" report, which was published by the state's own Innovation Advisory Council in 2021. Under "Bioeconomy, biotech and biopharma", the panel of experts advocates focusing on biomedicine in order to play a pioneering role in sustainable pharmaceutical development. The publisher is the Saxon State Chancellery.

Funding for bioeconomy
The Saxon state government supports the bioeconomy in various contexts. With the "Transfer workshops - innovation potential of the bioeconomy in Saxony" project, for example, the Free State aims to promote the transfer of bioeconomic innovations from science to industry, especially SMEs. The Free State is also involved at a global level. As part of the ERA CoBioTech network, transnational collaborative projects on the topic of "Biotechnology for a sustainable bioeconomy" are funded together with 21 organizations from 18 countries. One of the aims of CoBioTech is to strengthen Europe's global position in the biotechnology sector.
In order to develop bio-based processes and products, Saxony's bioeconomy players also receive support from the Federal Ministry of Research, Technology and Space (BMFTR). One example of this is the award of a contract for the establishment of a large-scale research center in Delitzsch - the Center for the Transformation of Chemistry - with the aim of establishing a sustainable circular economy for chemical products based on renewable raw materials.
Database search
Find your partners for research, production and supply.
For further questions please contact:

Tina Jaehnig
Industry, Innovation & Marketing
+49-351-2138 138